half life formula pharmacology
For drugs with first order kinetics this is a constant. Within the PK the steady-state is a concept of fundamental importance in pharmacology.
For more tutorials see our pharm playlist at.
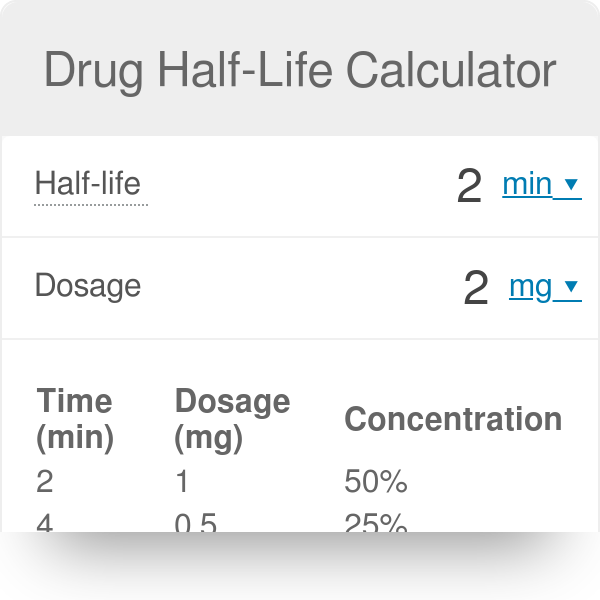
. The elimination half-life is considered to be independent. The half-life of a pharmaceutical refers to the amount of time it takes for the concentration of that substance in the body to be reduced by one half. Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology.
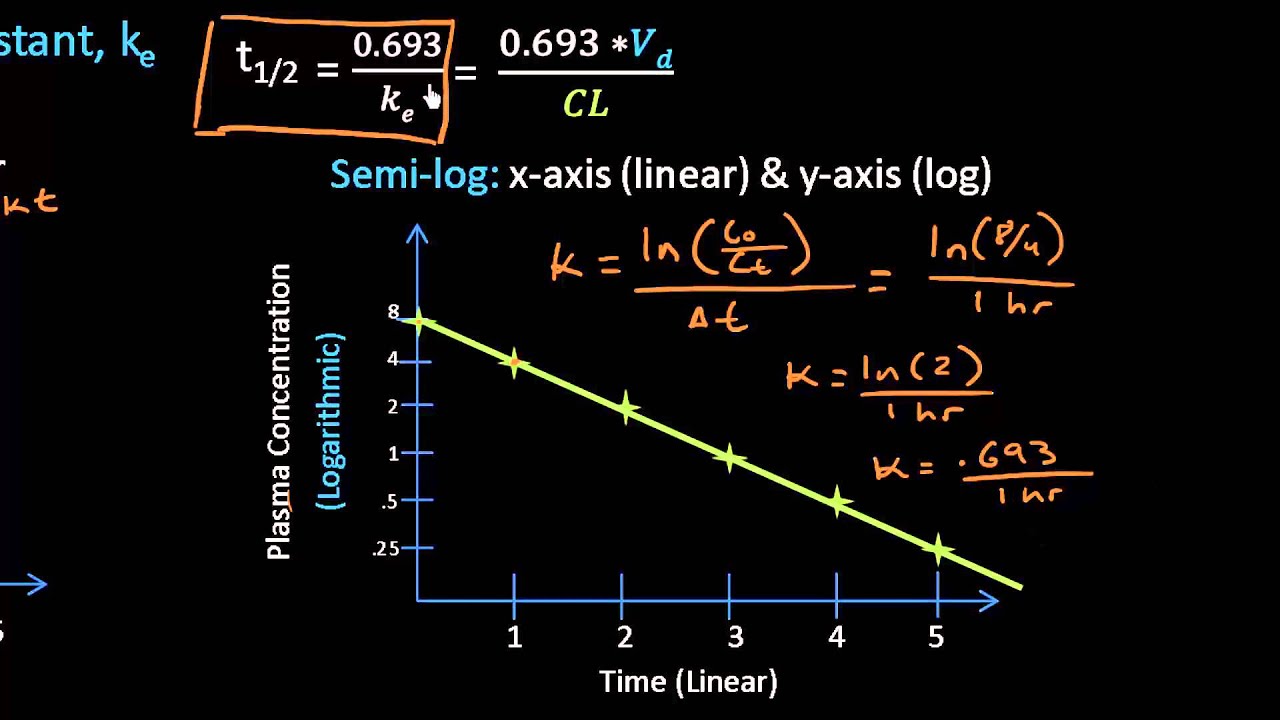
Half-life allows the calculation of the time required for plasma concentrations to reach steady-state after starting or changing a dosing regimen. The rest of the popcorn continues until the rest of the movie. The 0693 factor is in fact the logarithm of 2 which represents the fact that drug clearance typically occurs at an.
Half-life is used to estimate how long it takes for a drug to be removed from your body. Affiliation 1 Wyeth. It is the time in which the total amount of drug within the body after equilibrium of plasma with other compartment fatmuscle falls by one half or 50.
Pharmacology math tutorial for quick exam review. Biological half-life also known as elimination half-life pharmacologic half-life of a biological substance such as medication is the time it takes from its maximum concentration C max to half of its maximum concentration in the blood plasma and is denoted by the abbreviation. What is half life in pharmacokinetics.
The half-life of Ambien is about 2 hours. Half-life and Vd formulae are also. Formula Half Life 0693 KE Half Life 0693 0015 462 hours So this means that the drug will take 462 hours to remove roughly half.
A pharmacological definition and an analysis to its formula. Authors H Boxenbaum 1 M Battle. Where N0 refers to the initial quantity of the substance that will decay.
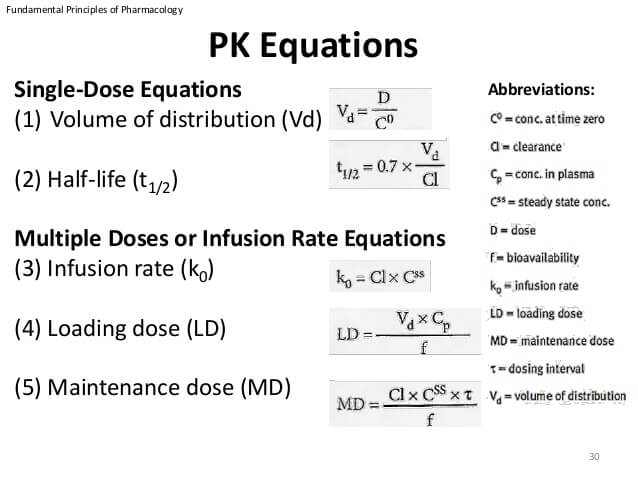
The formula for half-life is t½ 0693 Vd CL. What is Half Life. Intravenous bolus Initial concentration C D 0 Vd Plasma concentration single dose CCe kte 0 ae Plasma concentration multiple dose C Ce e kt k e e 0 1 Peak multiple dose C C e ke max 0 1 Trough multiple dose C Ce e k min ke 0.
It describes a dynamic equilibrium in which drug concentrations consistently stay within therapeutic limits for long potentially indefinite periods. The half-life can be calculated with the following formula. Irrespective of what the initial drug concentration.
The half-life of a drug depends on its clearance and volume of distribution. Formulas for half-life in exponential decay. How do you calculate half life in pharmacokinetics.
This is used to measure the removal of things such as metabolites drugs and signalling molecules. Learn the half life formula here. Half-life t½ is the time required to change the amount of a drug in the body by one-half during elimination.
A biological half-life or elimination half-life is the time it takes for a substance drug radioactive nuclide or other to lose. 109112 where N 0 is the initial. Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology.
Half-life t 12 1. So if you take Ambien after 2 hours the plasma concentration will. In biology and pharmacology.
The half-life of a drug is the time taken for the plasma concentration of a drug to reduce to half its original value. After 4 half-lives the amount of drug 625 is considered to be negligible regarding its therapeutic effects. Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology.
It is the time in which the concentration of the drug in plasma fall by 50. After one half-life the amount of drug remaining in the body is 50 after two half-lives 25 etc. Half-life refers to the amount of time it takes for half of a particular sample to react.
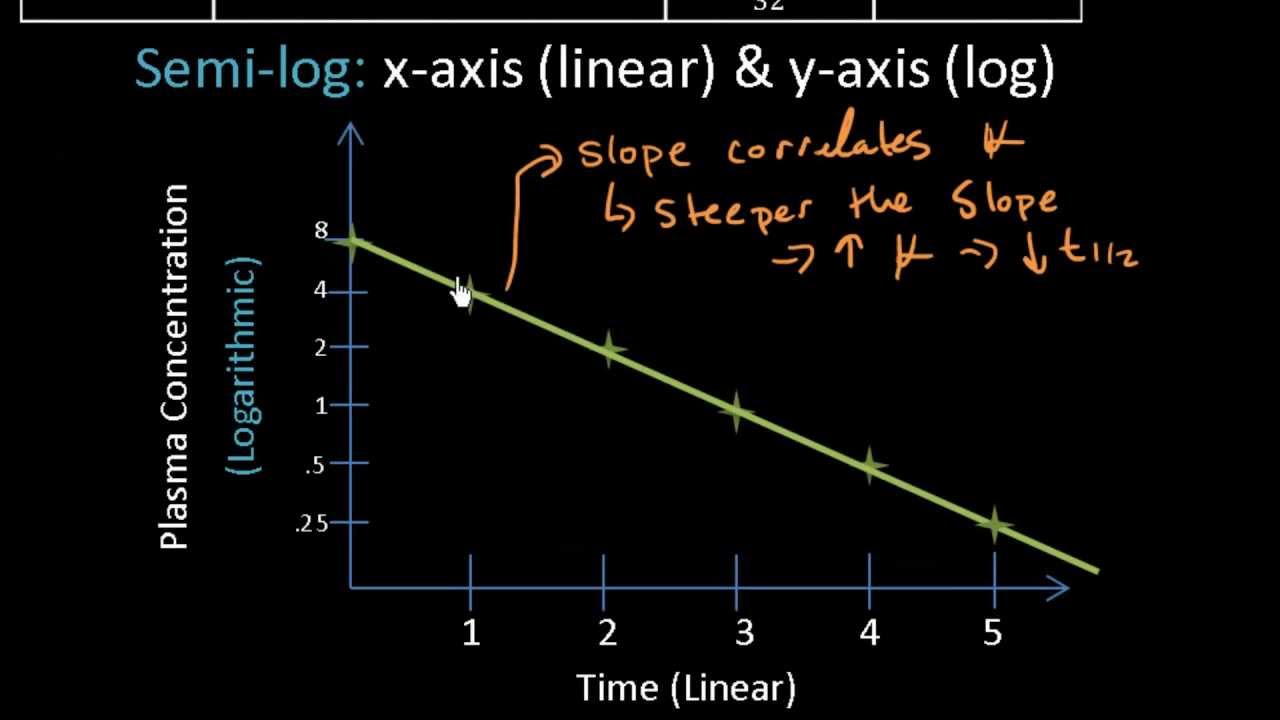
This can be measured by testing for the. An exponential decay can be described by any of the following four equivalent formulas. Substituting the value of C Co2 at t½ in equation 814 and solving it yields.
The two main factors which affect drug half-life are volume of distribution and clearance. The constant 07 in equation 6 is an approximation to the natural logarithm of 2. The formula for half life is t 1 2 l n 2 λ 0693 λ.
Half-life is useful because it indicates the time required to attain 50 of steady stateor to decay 50 from steady-state conditionsafter a change in the rate of drug administration. Half-life t Vd CL k kee 12 0693 2 0693 ln. By definition t 12 is the time required for the concentration to fall by one half.
40 mg drug is administered IV and after 2hr. Half life formula half life equation Half life 0693k. By definition t 12 is the.
Half-life t½ is the time required to reduce the concentration of a drug by half. T12 0693 K 816 Equation 816 shows that in contrast to zero-order process the half-life of a first-order process is a constant and independent of initial drug concentration ie. Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology J Clin Pharmacol.
Plasma half life t 12. The formula for half-life is t½ 0693 Vd CL Volume of distribution Vd and clearance CL are required to calculate this variable. Most noteworthy this shows that the rate of popcorn eating was not at a steady pace and that the half-life of popcorn is of 15 minutes.
Pharmacokinetics Mnemonics Epomedicine

Elimination Half Life An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Drug Half Life Explained Calculator Variables Examples
Loading Dose Pharmacology Flashcards Draw It To Know It

Pharmacokinetics Vd Clearance Half Life Calculation Drug Distribution Elimination Rate Youtube

Elimination Rate Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Half Life Pharmacology Flashcards Draw It To Know It

Half Life Calculator Radioactive Decay Calculator
First Order Elimination Rate Constant And Half Life A Closer Look Lect 11 Youtube